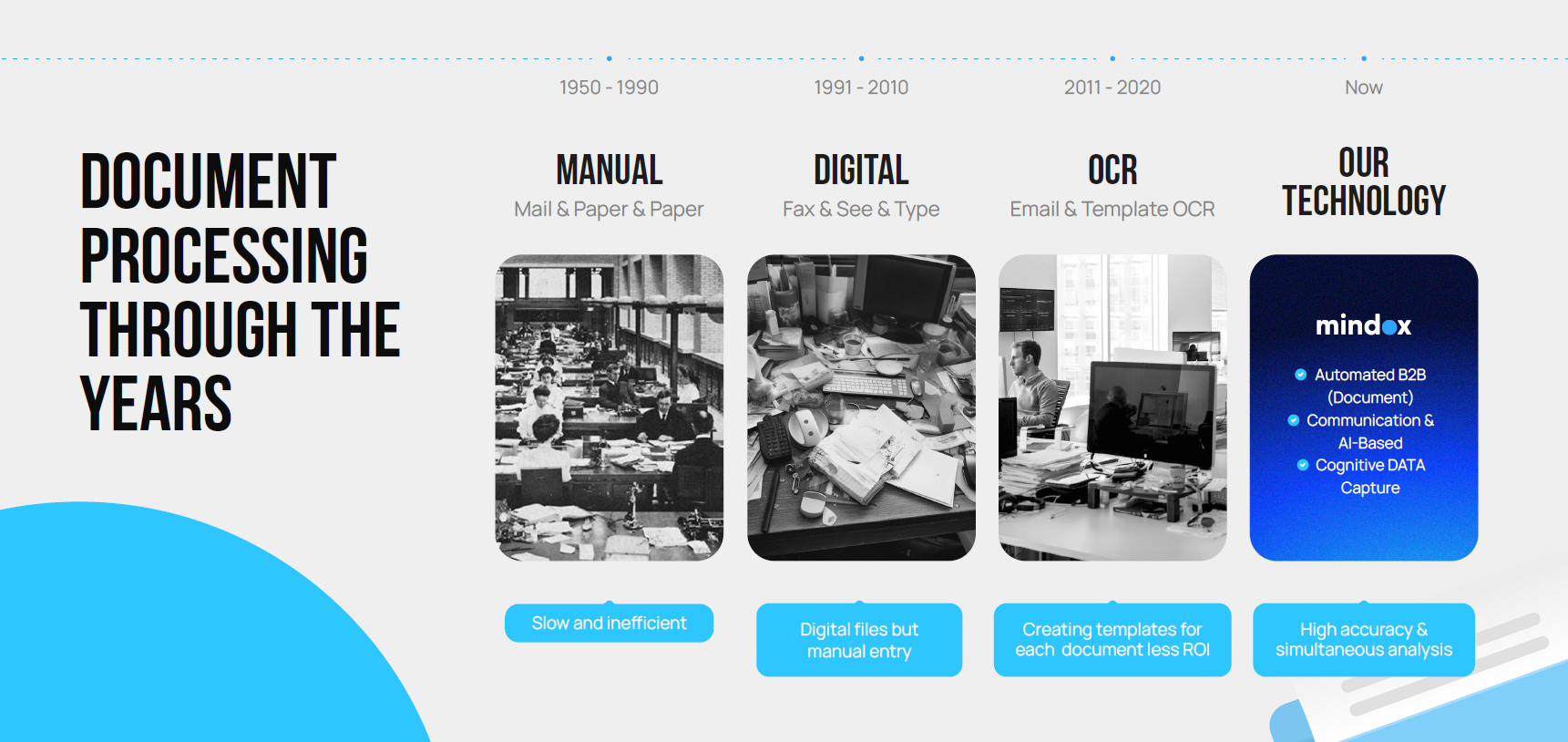
OCR : How It Works and Benefits Your Business


What is OCR?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a technology that converts different types of documents, such as scanned paper records, PDFs, or digital camera captures, into editable and searchable text data.
Here are some common uses of OCR technology:
- Automating data entry: Extracting information from paper documents to eliminate manual data entry tasks.
- Digitizing historical records: Converting physical documents into digital formats for easier access and storage.
- Enhancing accessibility: Making printed text accessible to visually impaired individuals through text-to-speech applications.
The Benefits of OCR
One of the most common uses of OCR is converting historical documents or legal paperwork into searchable and editable PDFs. This empowers users to work with these documents as if they were originally created on a computer. OCR unlocks a treasure trove of information that was previously trapped in physical form.
By automating data extraction and making documents digitally accessible, OCR streamlines workflows, improves efficiency, and reduces the risk of errors associated with manual data entry.
While OCR offers valuable automation, it has limitations:
While Optical Character Recognition (OCR) offers a powerful automation tool for extracting text from documents, it’s important to understand its limitations:
-
Accuracy Challenges: OCR can struggle with documents that have:
– Poor quality (blurry, faded, low resolution)
– Complex layouts (tables, mixed fonts, overlapping elements)
– Unconventional fonts (decorative, handwritten) These factors can lead to errors in data extraction, requiring manual correction.
-
Limited Context Awareness: OCR excels at recognizing characters but lacks the ability to understand the meaning or context behind the text. This can be problematic for tasks like sentiment analysis or data categorization.
-
Language and Format Barriers: Traditional OCR systems might not be fluent in all languages or recognize every document format. This limits their usability for diverse documents.
-
Manual Verification Often Necessary: Due to potential inaccuracies, OCR often requires human verification, especially for critical information extraction. This can negate some of the time-saving benefits.
A Case in Point: Invoices
A prime example of OCR limitations is processing invoices. Since invoices from different institutions often have unique formats (layout, fonts, data placement), a single, generic OCR template wouldn’t be effective. To achieve optimal accuracy, custom templates need to be created for each type of invoice to guide the OCR process and improve data extraction results.

Enter Intelligent Document Processing (IDP):
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) solutions, like mindox IDP, build upon OCR technology and add powerful features like Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to overcome the limitations mentioned above. Here’s how:
- Improved Accuracy and Speed: mindox leverages AI to enhance the accuracy of data extraction, even from complex and low-quality documents. This significantly reduces the need for manual intervention.
- Contextual Understanding: With NLP, mindox can understand the context and semantics of the text, enabling it to process a wider range of documents accurately.
- Versatility: mindox supports multiple languages and document formats, making it ideal for diverse applications, including loan processing in the Philippines.
- Automation of Complex Processes: Beyond simple data extraction, mindox can automate entire workflows, such as loan processing automation, by interpreting and acting on the extracted data.